I came across this sign on a recent visit to Washington, DC.

It redefines “voter suppression” as the presence of a nominating primary without instant runoff voting.
by Jack Santucci
I came across this sign on a recent visit to Washington, DC.

It redefines “voter suppression” as the presence of a nominating primary without instant runoff voting.
Alan Ware (2002, p. 231) writes the following. His book covered the politics of nominating primaries. Its key contribution was to argue that major-party leaders imposed direct primaries to help avoid party splits.
Maryland and Minnesota (both in 1912) had started to use the Alternative Vote electoral system for their primaries. The other possible solution for ensuring majority nominations – the run-off election – was deployed in six southern states, five of which had adopted it before 1917. Indeed, at various times other states had also used forms of so-called preferential voting to ensure that nominees were not the choice of merely a small minority.10 The solutions to the problem of vote fragmentation were well known. The far more intractable problems posed by direct primaries for the parties were, first, interest aggregation, because nomination decisions were now individualized, rather than being considered as part of a “package.” This increased the likelihood of intraparty tensions, and also the risk that unelectable tickets might result. The second problem was that the direct primary both reduced the ability of the party to control the “quality” of candidates selected, and in some cases made it more possible that wealthy individuals might triumph over poorer rivals having broader support among party activists.
Weeks (1937) gives the fullest account of these systems. Whether voters will use rankings sufficient to “guarantee” majority winners is an issue. There also is an open question in the literature: do single-seat reforms (like IRV) eventually induce coordination failure (so that voters do not use markings to get majority-supported outcomes)? Here is what Weeks says about these issues:
1. All states except Alabama and Oklahoma did not require the voter to register more than a first choice for any office. It seems to have been quite common in all the states indicated above that a great many voters failed to avail themselves of the privilege of registering second or more choices, which resulted in the practical restoration of the plurality system in many primary races. This failure was due to several causes: ignorance of the voter; his desire not to have his vote counted for any but his first choice; or his refusal to accept what was thought to be a complicated system, which, it was felt, could be easily corrupted or readily subject to mistakes in the count, or which seemed to provide for an unfair method of evaluating choices.
2. Failure of party leaders and officials to educate the public in the use of the preferential feature, due partly to their opposition to it as a complicated device and one the results of which could not be easily anticipated.
Weeks’ article contains a table of the 11 states that used IRV or the Bucklin system within primaries. Four had gone to runoffs by 1931. Six had gone to plurality. One more (Maryland) continued using a ranked-ballot system through 1937.
I touched on these issues here (pp. 177-180). The topic would make for an interesting research project.
Today was primary day in Philly. Below is a portion of the ballot. I found myself relying on the “Vote for not more than X” instructions.
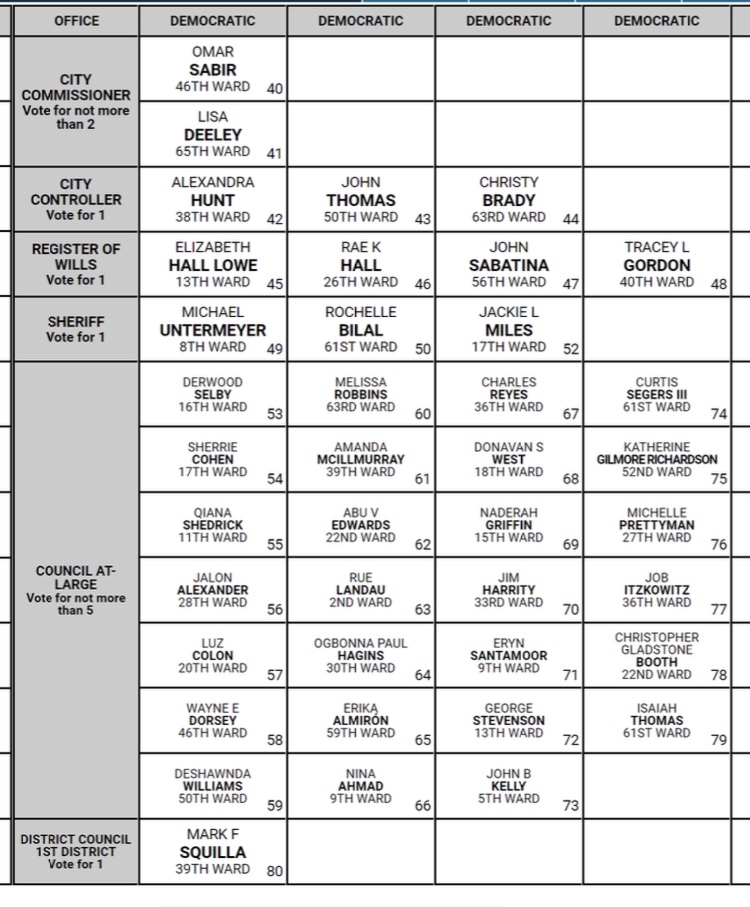
The race of interest is council-at-large. Here we are selecting five Democratic nominees to contest seven seats in November. (No party may give its label to more than five.)
This is where I pitch the “one-vote system.” All of the above candidates could run in the general without spoiling their party. There would be no further need to limit nominations by law. And the act of voting would be more user-friendly.